Fibre Optic internet is popular for businesses looking to boost productivity. We’ll explain how these tiny glass tubes of light can transfer anything from emails to high-definition videos anywhere around the world.
First Off, What’s in a Fibre Optic Cable?
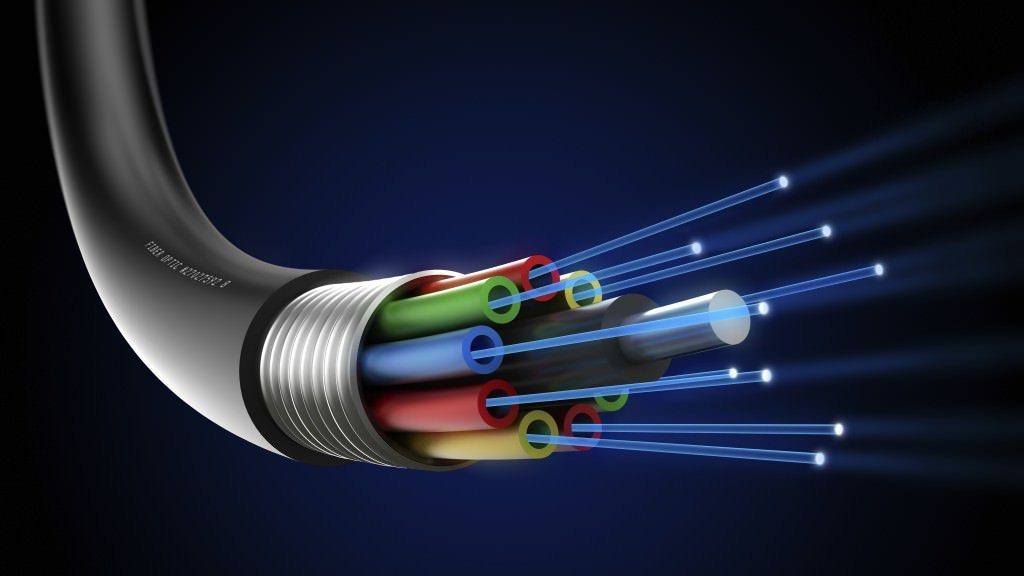
A common fibre cable has 5 layers:
1.Core
The central and most important layer is the core – made up of thousands of glass tubes bundled together and supported by a central strength element (e.g. a metal rod).
2.Cladding
Surrounding the core is a protective sheath of cladding. This increases the core’s total internal reflection to prevent data loss.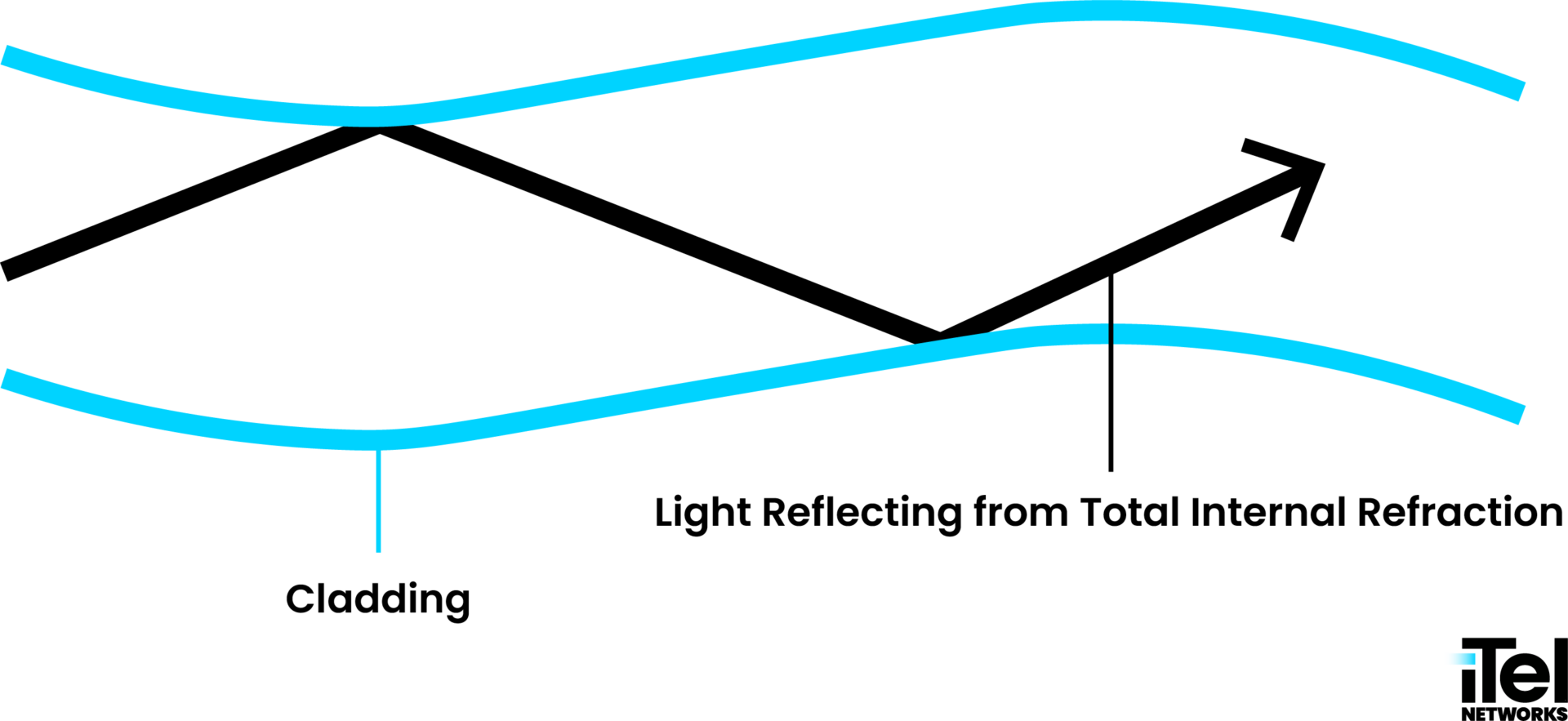
3.Plastic Coating
Reinforcing the core and cladding is a plastic coating.
4.Strengthening Fibres
The fourth layer of a fibre optic internet cable is made of strengthening fibres for added support.
5.Cable Jacket
To protect against elements, the layers are wrapped in a cable jacket. This outermost layer is found on all cables and wires.
What is total internal reflection?
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection happens when light reflects (instead of passing through) after hitting a shallow angle, like bouncing off a mirror. As light travels through the fibre optic cable, total internal reflection causes it to bounce off the cladding walls and stay inside the tube.
How do Fibre Optic Cables transmit data?
Data signals go through three stages when transmitting through fibre optics. Let’s take “liking a post on Facebook” for example:
Stage 1:
After clicking “like” on your coworker’s witty post, that action becomes an electric data signal sent to your internet transmitter. The transmitter then converts the data into a light signal by changing its pulse and intensity.
Stage 2:
Light signals travelling long distances pass through regenerators along the way to get boosts and avoid attenuation.
Stage 3:
Thanks to the boosts, a strong, attenuation-free signal arrives at the destination. The destination’s transmitter receives the signal and decodes it back to digital format to complete the transmission. You have officially liked that Facebook post!
Does Your Business need Fibre?
Investing in a fibre upgrade can empower the collaboration and communication your business needs to grow. As a business-exclusive internet service provider, iTel provides enterprise-quality fibre optic internet for businesses in every vertical. Contact us to learn more.