Wavelength Services – also called Wave Circuits – are the gold standard when it comes to moving large amounts of data. Moreso than even dedicated circuits, Wavelengths provide massive bandwidth capacity at a reasonable price.
If your business has heavy data processing requirements, you’ve probably already done a lot to improve your connectivity. From QoS to continuity planning, you have a lot of options. So what is a Wavelength – and how does it fit into your scenario?
What is a Wavelength?
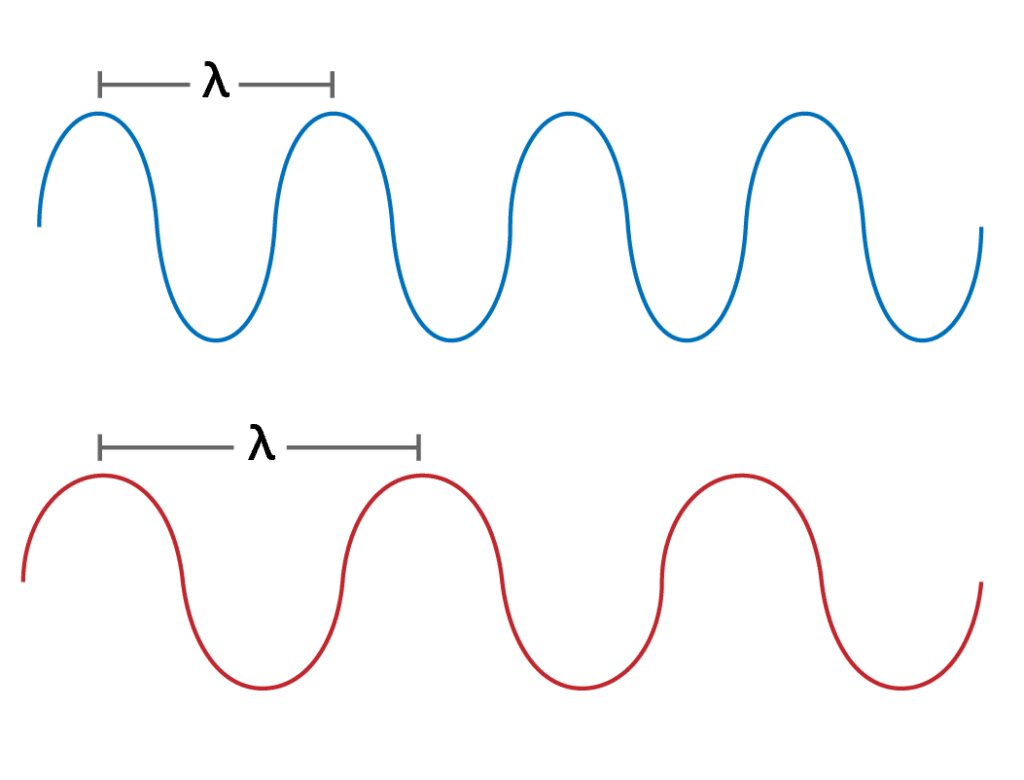
Figure 1 – Comparing peak-to-peak measurements of wavelengths.
Your old physics textbooks will define a wavelength (λ) as the distance between the peaks of waves (Figure 1) – aka a disturbance that moves energy from point a to point b. These peaks refer to either the highest point or the lowest point (trough) of the wave. The material in which a wave occurs will affect the length and speed at which the wave travels.
All forms of energy are classified, segmented, transmitted, and differentiated by their wavelength. For example, visible light has a different wavelength than radio waves and within the visible spectrum, different wavelengths produce different colours.
Almost all telecommunications occur via electromagnetic waves moving from a transmitter to a receiver. Fibre optic cables use infrared rays which have longer wavelengths than visible light to minimize attenuation via absorption and scattering. The maximum wavelength commonly seen in fibre cables is around 1550 nanometres(nm) as anything greater can release heat and disrupt the signal.
More specifically, the name “Wavelength” comes from Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM). This is a method of data transmission that can identify and separate closely-spaced waves on a fibre optic cable and redistribute them efficiently.
What’s the benefit of using Wavelength Services?
Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (Figure 2) means your provider can reserve a specific wave of light for your use only. Essentially, when you’re not using it, no one is using it! Think of the fibre cable as a highway – in busy areas, there may be a high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lane available to carpoolers and buses. WDM designates an entire wavelength as your personal “HOV lane” – and all your data as priority traffic.
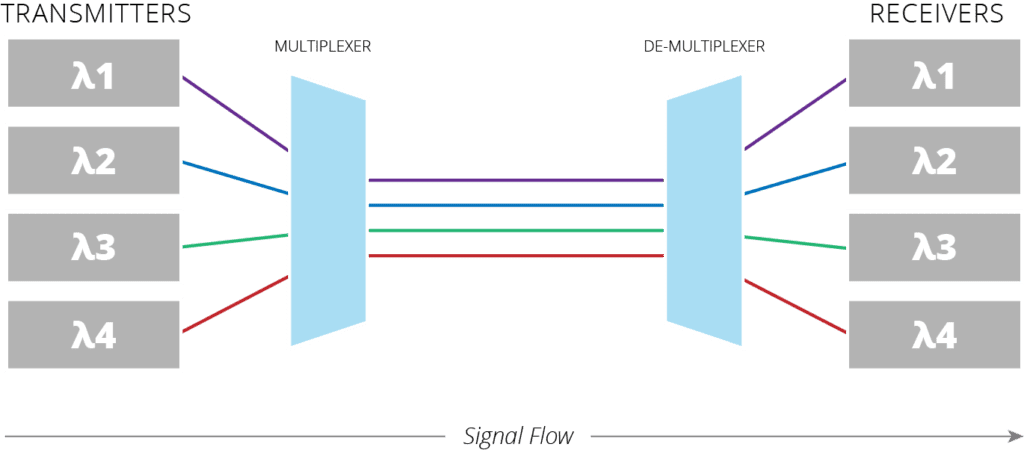 Figure 2 – Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) visualized[/caption]
Figure 2 – Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) visualized[/caption]
The result is that you always have a high bandwidth profile available for your data. You can get this bandwidth other ways, but using a Wavelength is often faster, more cost-effective, and more secure. iTel Wavelength services work on Layer 1 of the OSI model, so you get the lowest latency possible – at a great price. The same profile on ethernet will use more Layer 2 network resources in your provider’s core. These resources are expensive, and reserving them for your use comes at an increased cost!
Wave Circuits also provide improved security, as your data is fully separated from other clients who may also be using the connection. Adding encryption to your connection can boost your security even more.
What about Ethernet Dedicated Internet?
It’s worth keeping in mind that the high capacity of a Wave Circuit only makes sense for certain applications. If you just need an internet connection for browsing, email, etc., Wavelength Services aren’t going to make sense. Even with the most bandwidth-intensive use, there are better ways to connect to the public internet.
Compared to a Wavelength, Ethernet Dedicated Internet circuits work on Layer 2 of the OSI model. This consumes more of your provider’s core network resources and introduces more potential latency. As you add more OSI layers to a service, you add more potential for latency. This is rarely an issue for general connectivity, but if you’re processing large amounts of data in cloud servers, a Wavelength is going to start looking pretty good!
Once your applications start demanding 1 Gb or more – and become much more critical to your business! – moving your data on its own Wave Circuit makes sense. Until you hit that point, an Ethernet Dedicated Internet connection ensures you have fast, reliable internet. You’ll be guaranteed the bandwidth your team needs, with options for prioritizing traffic, Quality of Service (QoS) standards, and a Service Level Agreement (SLA) to back it all up.
But what about…
Your network design reflects your company’s needs and goals – and there’s rarely a one-size-fits-all approach that works! Here at iTel, we’ll provide you with an ethernet handoff so you can easily convert your wavelength to Layer 2. This means that you can connect the wavelength directly to your router or switch and utilize some of that “pipe” for internet connectivity. You really can have the best of both worlds!
iTel builds customized, flexible network solutions for companies of all sizes and configurations. Connect with our team today to start building your ideal network solution and learn more about iTel Wavelengths!